Among the various components of the building envelope, the roof performs multiple functions, including protection, drainage, thermal insulation, and aesthetic expression. As a key element of the roofing system, the structural form of roof tiles largely determines a building's durability, stability, and visual appeal. With the strengthening of domestic manufacturing capabilities, the variety of China Roof Tile Factory structures has increased, and production technologies and material processes have continuously evolved, resulting in significant differences in performance and suitable applications among different tile types. We are focuses on the common roof tile structures produced in domestic factories, analyzing their structural characteristics, performance variations, and application advantages, providing a reference for architectural design, construction, and materials research.

What are the common structural types of roofing tiles in China?
Currently, roof tile structures produced in domestic factories mainly include: single-layer tiles, double-layer tiles, S-shaped tiles, flat tiles, Roman tiles, French tiles, and interlocking tiles. The choice of structure is influenced by climatic requirements, roof slope characteristics, and visual aesthetics.
To provide a clearer overview of the basic characteristics of each structure, the following table summarizes the main types:
Overview of Domestic Roof Tile Structures
| Structure Type | Basic Form | Common Materials | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-layer tile | Single thickness structure | Clay, ceramic, cement | Lightweight, simple structure, easy installation |
| Double-layer tile | Upper and lower layers | Clay, ceramic | Improved drainage, stronger wind resistance |
| S-shaped tile | Wavy curved surface | Clay, concrete | Natural drainage, suitable for steep roofs |
| Flat tile | Flat, right-angle lines | Ceramic, cement | Modern appearance, clear geometric arrangement |
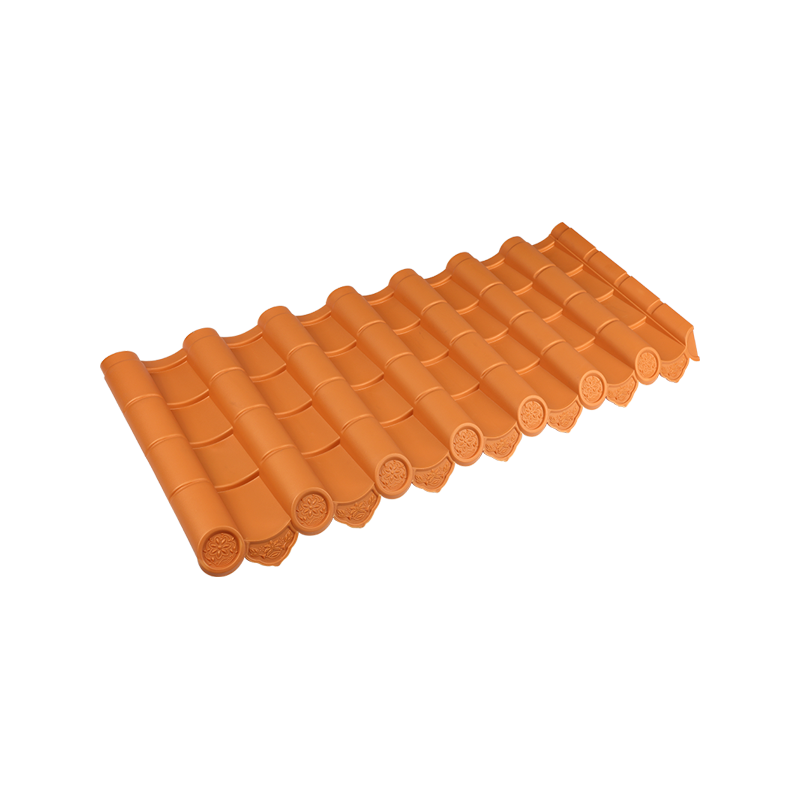
| Roman tile | Combination of curved and flat | Clay | Rich texture, strong decorative effect |
| French tile | Shallow wave structure | Clay | Regular lines, balanced drainage |
| Interlocking tile | Edge with locking slot | Various materials | Strong sealing, suitable for rainy and windy environments |
These structural forms not only influence the overall visual style of the roof but also determine drainage paths, wind load resistance, and maintenance requirements.
What are the performance differences between different structural forms?
1. Differences in Drainage Paths and Rainwater Management
Drainage performance is one of the most critical considerations in roof tile design.
S-shaped tiles and Roman tiles
The curved surface forms natural channels, allowing rainwater to flow quickly along the valleys, making them highly suitable for steep roofs.
Flat tiles
Drainage relies on the gaps between tiles. High installation precision is required, and improper laying may to localized water accumulation.
Double-layer tiles
The upper layer provides coverage while the lower layer guides water flow. The dual drainage paths enhance stability, making them suitable for areas with prolonged rainfall.
2. Differences in Wind Resistance
The structural design of tiles directly affects the roof's ability to withstand wind loads.
Interlocking tiles
The edge slots allow tight connections, reducing the risk of tiles being lifted by wind.
Double-layer tiles
Heavier weight combined with the interlocking upper and lower structure makes them more suitable for high-wind areas.
Flat tiles
Wind resistance depends largely on precise placement and the use of fasteners.
3. Differences in Visual Effects
Different tile structures create distinct architectural styles.
S-shaped and Roman tiles
Strong curvature, suitable for traditional, vintage, or Mediterranean-style buildings.
Flat tiles
Clear outlines, ideal for modern architecture, minimalist style, or simple roof designs.
French tiles
Shallow waves create a more regular visual effect, suitable for public buildings or long ridge roofs.
4. Differences in Material Compatibility and Durability
Materials play an important role in structural design, and different materials exhibit distinct performance characteristics:
| Material Type | Features | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic tile | High-temperature firing, frost-resistant, weather-resistant | High environmental requirements, long service life |
| Clay tile | Environmentally friendly, stable, natural color | Commonly used in traditional roofs |
| Cement tile | Stable weight, moderate cost | Requires surface coating and more maintenance |
The combination of structure and material determines the service life, color durability, and weather resistance of roof tiles.
What are the advantages of various roofing tile structures?
1. Advantages of Single-Layer Tiles
Single-layer tiles use a uniform thickness design with a simple, straightforward structure, making them one of the most widely used forms in traditional roofing applications.
Key Advantages:
Lightweight
The single-layer structure reduces roof load, making it suitable for lightweight buildings sensitive to structural loads.
Flexible Installation
Installers can easily adjust the tile layout according to tile size and roof slope, accommodating regional construction practices.
Low Maintenance Cost
The simple structure minimizes complex gaps, making subsequent maintenance relatively easy.
Material Compatibility
Can be made from clay, ceramic, or cement, allowing manufacturers to adjust formulas and processes according to project requirements.
Single-layer tiles are typically used in residential buildings, balancing cost, drainage stability, and ease of installation.
2. Advantages of Double-Layer Tiles
Double-layer tiles consist of an upper layer for coverage and a lower layer for support, providing improved stability in rainwater management and wind resistance.
Key Advantages:
Dual Drainage Path Enhances Stability
The upper layer provides a primary drainage route, while the lower layer guides water, reducing the risk of water reaching the bottom layer.
Superior Wind Resistance
The layered structure increases weight and forms interlocking connections, enhancing resistance to external forces.
Strong Coverage
The upper tile is typically wider, covering joints between adjacent tiles and reducing the risk of water infiltration.
Tighter Installation
Double-layer structure controls gaps between tiles, creating a more integrated roofing system.
Double-layer tiles are suitable for areas with frequent rainfall, high wind, or high waterproofing requirements.
3. Advantages of S-Shaped Tiles
S-shaped tiles have a wavy, curved appearance and are commonly used on sloped roofs.
Key Advantages:
Natural Drainage
The wave valleys naturally guide water flow, allowing fast drainage on steep roofs.
Strong Three-Dimensional Effect
The height difference between wave peaks and valleys creates pronounced light and shadow effects, enhancing roof texture.
Improved Wind Flow Adaptation
The wavy structure disperses wind impact, reducing the likelihood of tiles being lifted.
Suitable for Long Slopes
Overlapping waves form continuous drainage channels, ideal for large residential or sloped roof buildings.
S-shaped tiles are particularly suitable for traditional, Mediterranean-style roofs or projects emphasizing roof aesthetics.
4. Advantages of Flat Tiles
Flat tiles feature straight lines, often with small side folds or grooves to improve drainage and interlocking.
Key Advantages:
High Compatibility with Modern Aesthetics
Clean, flat surfaces visually integrate with materials like glass and metal.
Flexible Geometric Layouts
Can be installed in straight, staggered, or fish-scale patterns for diverse visual effects.
Better Roof Flatness
The flat structure provides a neat overall shape, suitable for large public buildings or villa roofs.
Reduced Wind Exposure
Smaller wind-facing area and tight installation reduce the risk of displacement.
Flat tiles are widely used in modern, minimalist, commercial, or urban residential projects.
5. Advantages of Roman Tiles
Roman tiles combine curved and flat surfaces, creating a rhythmic and decorative roof appearance.
Key Advantages:
Improved Drainage Efficiency
Curved areas guide water while flat areas provide stable coverage, creating a balanced drainage system.
Rich Visual Layers
Slightly lower curvature than S-shaped tiles, but arrangement produces noticeable rhythmic patterns, enhancing aesthetics.
Good Stability
Larger tile sizes reduce the number of pieces, improving overall roof integrity.
Flexible for Various Slopes
Less strict slope requirements than S-shaped tiles, making them adaptable to medium-pitched roofs.
Roman tiles are ideal for villas, cultural buildings, or projects requiring traditional roof aesthetics.
6. Advantages of French Tiles
French tiles usually have shallow wave patterns, providing neat, fine, and linear appearance.
Key Advantages:
Regular and Uniform Lines
Suitable for projects demanding consistent roof appearance, such as schools, factories, or exhibition halls.
Balanced Drainage
Shallow waves provide moderate water flow, preventing excessive drainage speed and maintaining roof pressure stability.
Moderate Weight
Medium thickness balances structural load and durability.
Suitable for Large-Area Installation
Creates a consistent line pattern across large roof spans, minimizing visual clutter.
French tiles are favored for their neatness and visual consistency, widely applied in public and cultural buildings.
7. Advantages of Interlocking Tiles
Interlocking tiles feature edge slots for "snapping" connections and have become increasingly popular in recent years.
Key Advantages:
Enhanced Sealing
Slots reduce gaps, improving waterproofing, suitable for regions with heavy rain or snow.
Stronger Wind Resistance
Interlocking structure forms a locally integrated system, making tiles harder to lift.
High Installation Tolerance
Slots limit tile positioning, reducing human error and unevenness.
Adaptable to Complex Roof Shapes
Handles corners, edges, and other challenging areas, reducing trimming work.
Easier Maintenance
Interlocking design allows quick replacement of individual tiles without large-scale removal.
Interlocking tiles are widely used in coastal areas, mountainous regions with high wind, or projects requiring highly reliable roofing systems.
How to Choose Roof Tile Structures for Building Projects?
In actual building projects, selecting the appropriate roof tile structure requires a comprehensive evaluation of building type, local climate, maintenance cycle, and construction conditions.
1. Match Tile Strength and Durability to Building Use
Different building types have distinct requirements for roofing materials:
Public buildings and large facilities
Require higher load capacity, durability, and wind resistance. Recommended choices include:
- Double-layer tiles
- Thick cement tiles
- High-density ceramic tiles
These structures perform better in terms of compressive strength, crack resistance, and long-term stability.
Residential buildings
Focus more on roof appearance, thermal stability, and ease of maintenance. Common selections include:
- Single-layer clay tiles
- Glazed ceramic tiles
- Lightweight composite tiles (for structures with limited load capacity)
Lightweight steel-frame buildings
Prefer lightweight, quick-install structures, such as:
- Interlocking tile systems
- Embedded lightweight tiles
This reduces overall roof load and installation effort.
2. Choose Structure Sealing Based on Climate Conditions
Climate is a key factor in roof tile selection, as different structures vary in resistance to wind, rain, snow, and temperature changes:
Cold regions (heavy snow, large temperature differences)
Recommended:
- Double-layer tiles
- Thick ceramic tiles
- Sloped interlocking structures
Reason: High structural strength, excellent frost resistance, and tight joints reduce the risk of water infiltration from melting snow.
Hot regions (strong sunlight, large temperature swings)
Recommended:
- Glazed clay tiles
- Single-layer ventilated tiles
Reason: Glazing reduces heat absorption, and ventilation mitigates stress from thermal expansion and contraction.
High rainfall areas
Recommended:
- Interlocking tiles
- Deep wave tiles
Reason: Faster drainage and reduced lateral water penetration.
Coastal or high-wind areas
Recommended:
- High-center-of-gravity thick tiles
- Closely interlocked tiles
Reason: Strong wind resistance and structural stability.
3. Decide Tile Structure According to Roof Slope
Roof slope affects water drainage and overall roof stability:
Low-slope roofs
Focus: Waterproofing
Recommended structures:
- Wide-overlap tiles
- Interlocking waterproof tiles
Medium-to-high slope roofs (typical residential slopes)
Focus: Drainage efficiency and aesthetics
Recommended:
- Single or double-layer clay tiles
- Wavy structured tiles
Very steep roofs
Focus: Slip resistance and secure fixing
Recommended:
- Deep-groove tiles
- Reinforced hook-mounted tiles
Different slopes require adjustments in tile overlap length and fastening methods. More complex tile structures adapt better to varying slopes.
4. Select Structure Based on Construction Method and Maintenance Cycle
Roof tile structure affects both installation and long-term maintenance:
Easy-to-maintain structures
- Single-layer clay tiles
- Standard wave tiles
Characteristics: Simple structure, easy to remove and replace.
Durable structures
- Double-layer tiles
- High-density ceramic tiles
Characteristics: High crack resistance, low displacement, suitable for long-life buildings.
Projects with high construction speed requirements
Embedded or interlocking tiles
Characteristics: Quick assembly, reducing labor and construction time.
5. Choose Tile Appearance According to Architectural Style
Different tile structures create distinct visual effects, making style an important factor:
- Traditional style: Barrel tiles, S-shaped tiles, antique clay tiles
- Modern style: Flat tiles, shallow-wave tiles, uniform-sized tiles
- Sloped residential roofs: Wavy tiles, single-layer clay tiles
- Large public buildings: Symmetrically arranged thick tiles, deep interlocking structures
Visual style and tile structure complement each other, affecting the overall architectural impression.
6. Choose Tile Weight Based on Roof Load Capacity
The roof's load-bearing capacity determines suitable tile types:
High load-bearing roofs
- Thick tiles
- Double-layer tiles
- Reinforced cement tiles
Limited load-bearing roofs
- Lightweight composite tiles
- Fiber-reinforced tiles
Heavier tiles offer more stability but require stronger building foundations. Project designers should select tiles according to actual structural capacity.
Why Choose Chuanya Building's China Roof Tile Factory?
Stable Raw Material Processing Ensures Uniform Tile Density
Through standardized batching and continuous mixing, the tile body contains fewer impurities and pores, helping to reduce cracking and deformation during later stages.
Wide Range of Structural Forms to Meet Different Building Needs
Available structures include single-layer, double-layer, interlocking, and wavy tiles, allowing flexible selection based on roof slope, climate conditions, and architectural style.
Well-Controlled Firing Temperature Enhances Structural Stability
The kiln's heating, holding, and cooling stages are carefully controlled, ensuring manageable internal tile stress and improved resistance to cold and heat.
Minimal Size Deviation Facilitates Neat Installation
High mold precision and consistent forming result in more orderly tile alignment and better sealing at overlaps.
Variety of Surface Finishes to Match Architectural Styles
Options include glazed, matte, and natural colors, allowing tiles to meet functional requirements while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Suitable for Long-Term Roof Systems
High production stability contributes to overall tile durability, making them well-suited for large-scale, long-lasting building projects.
Domestic roof tiles are increasingly diverse, functional, and refined in structural forms. Different tile types emphasize various aspects of drainage, wind resistance, and visual effect based on their material characteristics, forming methods, and design logic. As domestic building demands continue to diversify, structural innovation in roof tiles is expected to advance further, providing greater value in both engineering and architectural design.















 Email:
Email: Phone:
Phone: Adress:
Adress: