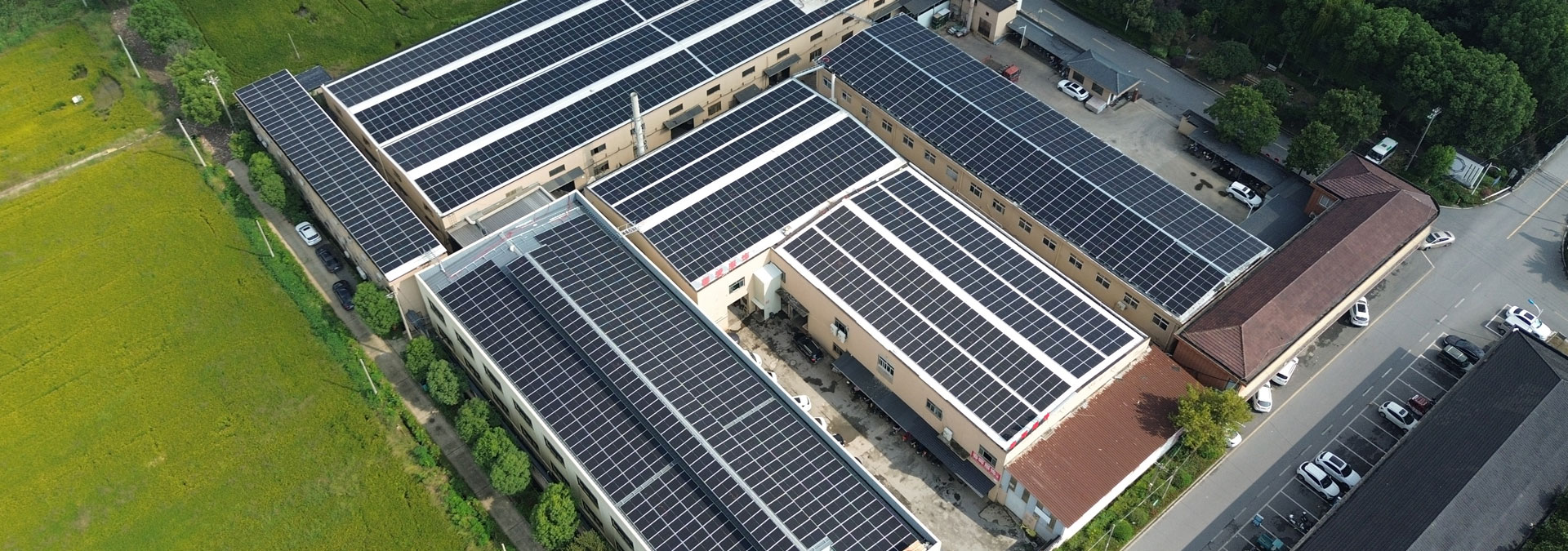
Factory Building Roof Tiles are a key element in industrial and commercial construction, providing protection, insulation, and structural support for various types of buildings. While commonly associated with factories, these roof tiles are also widely used in warehouses, storage facilities, and other large-scale industrial structures. The roof not only shields interiors from weather conditions but also affects ventilation, energy efficiency, and the overall environment inside the building.
Advances in materials and design have expanded the options for roof tiles, making them more durable, versatile, and suitable for different climatic conditions. Understanding their types, manufacturing processes, installation considerations, and maintenance practices is essential for architects, engineers, and facility managers who aim to ensure long-lasting and efficient roofing solutions across multiple building types.

What are the Different Types of Roof Tiles
Roof tiles used in industrial and commercial buildings come in a variety of materials and designs, each offering specific characteristics for different construction needs. Understanding these types can help professionals choose the most suitable solution for their projects, considering factors such as durability, climate, and structural requirements.
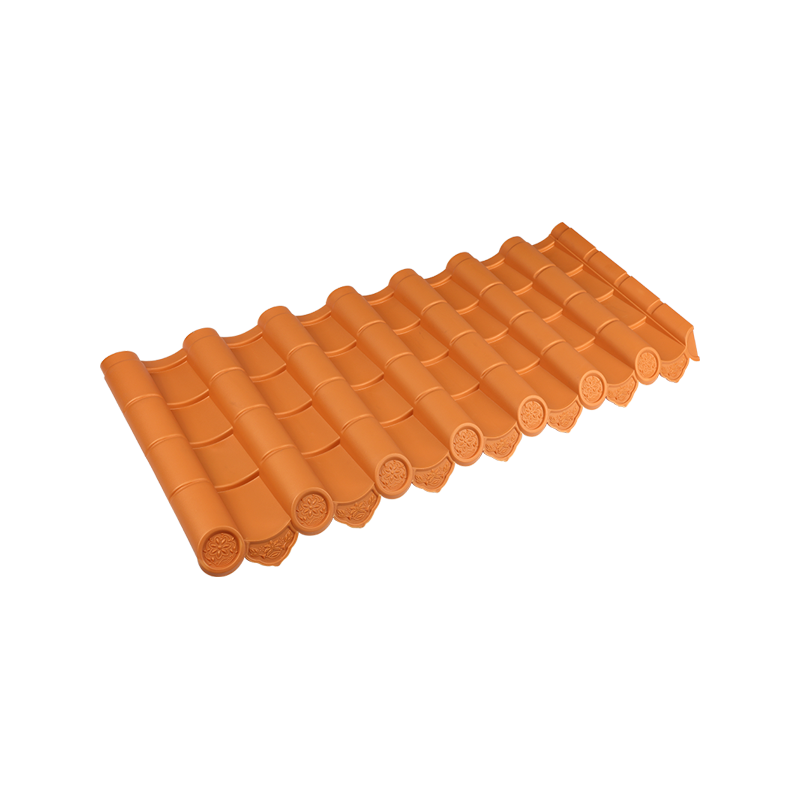
1. Clay Roof Tiles
Clay tiles have been utilized in construction for centuries. They are known for their natural resistance to weather changes and their ability to retain shape over long periods. These tiles can provide a stable roof structure while contributing to the aesthetic appearance of large buildings. Although their weight requires careful structural planning, clay tiles remain a common choice for warehouses and industrial facilities that prioritize long-term durability.
2. Concrete Roof Tiles
Concrete tiles are formed using a mixture of cement, sand, and water, and then cured to achieve strength. They offer flexibility in design, allowing for varied shapes and colors. One notable feature is their ability to handle heavy loads and resist impacts, which makes them suitable for expansive roof surfaces where stability is important. Concrete tiles can also be produced in modular sizes, facilitating faster installation on larger buildings.
3. Metal Roof Tiles
Metal options, such as steel or aluminum-based tiles, have become increasingly popular in industrial construction. They are lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion when properly coated. Metal tiles can also reflect sunlight, which can contribute to temperature control within the building. Their adaptability allows them to be shaped into profiles that mimic other tile types while maintaining their structural advantages.
4. Composite Roof Tiles
Composite tiles combine different materials to create versatile solutions that balance durability, weight, and visual appeal. These products often integrate synthetic polymers with natural aggregates, providing resistance against cracking, moisture penetration, and temperature variations. Composite tiles are particularly useful in facilities that require both functional performance and design flexibility.
5. Specialty or Custom Tiles
Some projects may require tiles designed for specific purposes, such as enhanced insulation, fire resistance, or unique architectural forms. Specialty tiles are produced to meet these requirements without compromising the basic protective function of the roof. Industrial complexes, research facilities, and storage hubs sometimes employ these custom options to address unique structural or environmental conditions.
Summary Table of Roof Tile Types
| Type | Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | Weather-resistant, durable, heavy | Warehouses, industrial buildings |
| Concrete | Flexible design, strong, modular | Large factories, storage facilities |
| Metal | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, reflective | Commercial and industrial roofs |
| Composite | Balanced durability and flexibility | Multi-purpose industrial buildings |
| Specialty/Custom | Tailored for insulation, fire, or design needs | Unique industrial and commercial projects |
Each of these roof tile types presents specific advantages and considerations, allowing construction teams to select options that align with project goals, environmental factors, and long-term maintenance plans. Awareness of material properties and practical applications ensures that buildings maintain structural stability, energy efficiency, and interior comfort over time.
How Are Roof Tiles Manufactured
Roof tile production is a mix of tradition and modern technology, with each material following its own journey from raw ingredients to finished product.
Clay Tiles:
These often start with natural clay that is shaped under pressure. Some facilities still apply semi-traditional methods, giving the tiles subtle variations in texture. Such differences can affect how the roof handles heat, moisture, and long-term wear.
Concrete Tiles:
Concrete tiles rely on precise mixing and curing. Automated systems help maintain uniform strength and shape, while modular designs make installation on large surfaces more efficient.
Metal Tiles:
Metal options are rolled, stamped, or pressed into shape. Coatings can enhance resistance to corrosion and reflect sunlight, helping manage building temperatures.
Composite Tiles:
Composite tiles blend polymers with natural aggregates. This approach balances weight, durability, and visual appeal, making them suitable for diverse industrial and commercial projects.
Quality Checks and Sustainability:
Continuous inspections during shaping, curing, and treatment ensure uniformity and reduce defects. Many manufacturers are also introducing energy-efficient production practices and material recycling, reflecting the industry's growing focus on sustainability.
Maintenance Tips for Extending the Life of Factory Building Roof Tiles
Roof tiles are durable, but like any construction material, they benefit from proper maintenance. Regular attention can prevent minor issues from turning into costly repairs, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the indoor environment. Here are practical tips:
Key Maintenance Areas
| Area | Why It Matters | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Early signs of damage or displacement | Walk the roof periodically, check for gaps or broken tiles |
| Cleaning & Debris | Moisture retention, moss, and dirt accumulation | Remove leaves, dust, and debris to prevent water-related issues |
| Fastening Check | Stability under wind and vibration | Ensure nails, clips, or adhesives remain secure |
| Weather Monitoring | Material expansion, contraction, and wear | Observe effects after storms and temperature changes |
| Underlayment & Seals | Prevent leaks and structural damage | Inspect underlayment, flashing, and seals regularly |
| Professional Checkups | Hidden problems not easily seen | Schedule periodic inspections by experienced personnel |
| Maintenance Records | Track roof performance and history | Document inspections, repairs, and observations for future reference |
Tips for Practical Use
- Short but Frequent Checks: Small, regular inspections can catch problems early without interrupting building operations.
- Safe Cleaning: Use soft tools and avoid harsh chemicals that may damage tiles.
- Plan Repairs Promptly: Addressing minor cracks or loose tiles quickly reduces long-term maintenance costs.
By focusing on these maintenance areas, industrial and commercial roofs can remain functional and reliable over time. Consistent attention ensures that the investment in roof tiles continues to protect buildings while supporting a comfortable and safe working environment.
How Factory Roof Tile Design Impacts Ventilation and Indoor Comfort
The design of roof tiles plays a more important role than many realize. Beyond protecting a building from weather, the way tiles are shaped, layered, and positioned can significantly influence airflow, temperature regulation, and indoor comfort.
1. Roof Profile and Airflow
The shape and slope of tiles affect how air moves across and under the roof. Curved or interlocking designs can promote natural ventilation, allowing hot air to escape while drawing cooler air inside. This reduces the reliance on mechanical cooling and helps maintain a more stable internal environment.
2. Material Selection and Heat Management
Different materials absorb and release heat at varying rates. Tiles that reflect sunlight or have insulating properties can reduce heat transfer into the building. Properly chosen materials help moderate indoor temperature fluctuations, which is especially important for industrial facilities where machinery generates extra heat.
3. Tile Spacing and Layering
Even small gaps or overlaps in tile arrangement can impact airflow and condensation control. Designs that allow slight movement of air between layers help prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to mold growth or structural deterioration over time.
4. Integration with Ventilation Systems
Some roof tiles are designed to work in conjunction with ridge vents, turbines, or other ventilation devices. This integrated approach ensures that air circulates efficiently, improving worker comfort and reducing energy costs for cooling systems.
| Design Element | Effect on Ventilation and Comfort | Practical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Profile & Slope | Enhances natural airflow | Reduces heat buildup inside buildings |
| Material Properties | Reflects sunlight, insulates | Stabilizes indoor temperature |
| Spacing & Layering | Controls condensation and airflow | Prevents moisture-related issues |
| Ventilation Integration | Supports mechanical or passive ventilation | Improves overall indoor air quality |
By considering these design factors, architects, engineers, and facility managers can optimize roof performance. Thoughtful tile design not only extends the lifespan of roofing materials but also contributes to healthier, more comfortable, and energy-efficient indoor environments.
Why Choose Chuanya Building for Factory Roof Tiles
At Chuanya Building, we focus on producing roof tiles that combine durability, versatility, and practical performance for industrial, commercial, and large-scale buildings.
We carefully select materials and use consistent production processes to ensure that every tile can withstand weather and the test of time. Our range of designs and profiles allows construction teams to find solutions that fit different building types and climates.
We also consider long-term maintenance and indoor comfort. Our tiles are designed to simplify upkeep, help control temperature and ventilation, and support safe and comfortable working environments.
By choosing us, builders and facility managers gain access to roofing solutions that are both functional and adaptable, helping projects run smoothly while protecting occupants and assets.



 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى








 Email:
Email: Phone:
Phone: Adress:
Adress: